explain
Indexes are used to find rows with specific column values quickly.
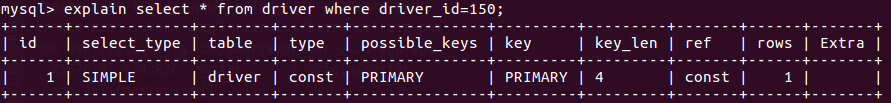
- id (query id) - 查询执行的顺序
- select_type (type of statement) - 查询的类型
SIMPLE,简单查询,不使用UNION或子查询等。PRIMARY,子查询中的最外层查询。UNION,UNION中的第二个或后面的select查询。SUBQUERY,子查询中的第一个select,结果不依赖于外部查询。DEPENDENT SUBQUERY,子查询中的第一个select,结果依赖于外部查询。DERIVED,派生表的select,from子句的子查询。
- table (table referenced) - 使用的表名,可能是表的别名。
- type (join type) - 连接的类型
ALL- Full Table Scan,全表查询index- Full Index Scan,只遍历索引树。range- 只检索给定范围的行且使用索引。ref- 连接匹配条件,即哪些列或常量被用于查找索引列上的值。eq_ref- 类似ref,区别是使用的索引是唯一索引,对于每个索引值表中只有一条记录匹配。const、system- 当mysql对查询某部分优化并转换为一个常量时,使用这些类型访问。例如将主键置于where条件中,MySQL就能将该查询转换为一个常量。system是const的特例,当查询表中只有一行记录时。NULL- 优化后甚至不需要访问表或索引,如取最小值可通过单独索引完成查找。
- possible_keys (which keys could have been used) - 可能使用到的索引
- key (key that was used) - 实际使用到的索引,若没有任何索引则显示为null
- key_len (length of used key) - (实际使用的)索引的长度
- 表示索引中使用的字节数(通过定义得到的理论值)
- ref (columns compared to index) - 列与索引的比较,表示上述表的连接匹配条件,即哪些列或常量被用于查找索引列上的值
- rows (amount of rows searched) - 扫描的行数
- Extra (additional information) - 额外的信息
Using index- 使用了索引覆盖。Using where- 不用读取表中的数据,只通过索引就能完成查询。即通常所说的索引覆盖。Using filesort- 当含有order by操作,且无法通过索引完成排序。Using join buffer- 连接条件没有使用索引,且需要连接缓冲区来存储中间结果。通常是一个需要优化的信号。Impossible where- where语句可能导致没有符合条件的行。Select tables optimized away- 仅通过使用索引,优化器可能仅从聚合函数结果中返回一行。如MIN/MAX/MyISAM引擎中的Count(*)No tables used- Query语句中使用from dual(即空表)或不含任何from子句
高级用法
explain FORMAT=JSON select xxx from yyy where zzz;
查看用例
索引
用以高效查询数据的数据结构。
Hash索引
底层数据结构是哈希表,只能用于等值查询,在碰撞场景下效率低,无法利用索引完成排序,没有最左匹配特性。
B+树索引 - Innodb
底层数据结构是多路平衡查询树,节点天然有序,额外的适用于范围查询。
详细讨论参考另一篇文章
聚簇索引
通常就是主键索引。索引所在的页储存了数据行。
非聚簇索引
除聚簇索引之外其他的索引都称为非聚簇索引。索引所在的页只存储了主键值,若需要其他数据需要回表查询。
联合索引的索引覆盖
创建测试数据库
1 | |
explain FORMAT=JSON select subject,salary from teacher where name="Mozart";
输出:
1 | |
Using index (JSON property: using_index)
The column information is retrieved from the table using only information in the index tree without having to do an additional seek to read the actual row.
- 索引如何加速排序
- Mysql的ICP(Index Condition Pushdown Optimization)
- 索引的存储和缓存
- 索引区分度和索引长度
- …
联合索引的最左匹配原则
| 假设索引idx_a_b_c(`a`,`b`,`c`) | 索引是否使用 |
|---|---|
| where a=3 | |
| where a=3 and b=4 | |
| where a=3 and b=4 and c=5 | |
| where c=5 and a=3 and b=4 | |
| where b=4 / where b=4 and c=5 / where c=5 | |
| where a=3 and c=5 | |
| where a=3 and b>4 and c=5 | |
| where a is null and b is not null | |
| where a <> 3 and b=4 | |
| where a^3>0 | |
| where a=3 and b like 'k%' and c=5 | |
| where a=3 and b like '%k%' and c=5 | |
| where a=3 and b like 'k%k%' and c=5 |
索引下推 - Index Condition Pushdown Optimization
索引失效场景
参考资料:
