(最大)二叉堆是一个维护着最大堆属性的完全二叉树。
最大堆用来实现高效的优先级队列PQ(Priority Queue)。
为集中精力讨论二叉堆本身,本教学中的最大二叉堆中不包含相同的数值。
完全二叉树的定义:除最下层,其它层组成满二叉树(每个节点上都有值),而最下层的节点都靠左排列不留空隙。
最大二叉堆属性:每个节点的父节点(除了根节点),都比该节点大。
优先级队列:
Enqueue(x),将新元素x放入队列(按照某种次序)y = Dequeue(),将序列中优先级最大的值返回;若存在相同优先级的值,则返回最先插入的值,即退化到FIFO
最大二叉堆的高度 <= log N(二分)
完全二叉树可以高效的存储为数组,因为展开为数组之后,各节点之间没有空隙。为简化遍历操作,我们假设数组下标从1开始。
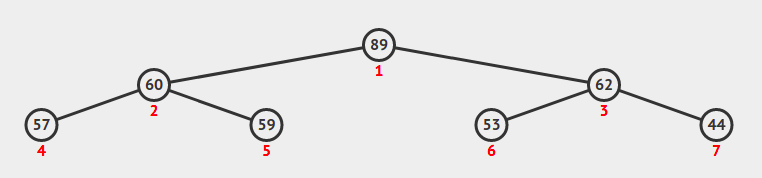
parent(i) = i>>1,例如8号节点的父节点为4号则parent(8) = 8>>1 = 4left(i) = i<<1right(i) = (i<<1) + 1
本教学中会介绍一下(最大)二叉堆的操作:
- Insert(v)
O(log N)
- ExtractMax()
O(log N)
- Create(A)
O(N log N)版本
- Create(A)
O(N)版本
- HeapSort()
O(N log N)
Inset(v)
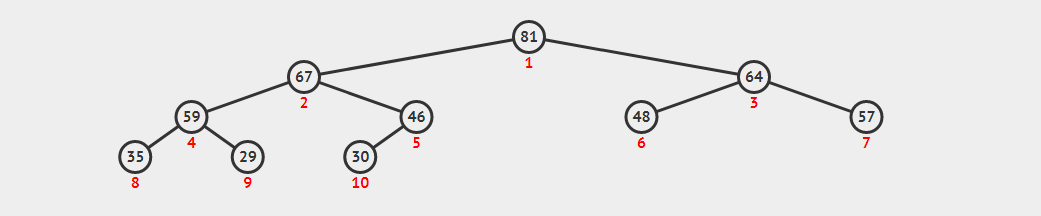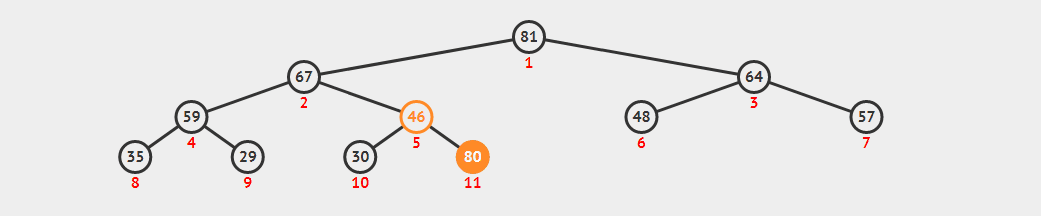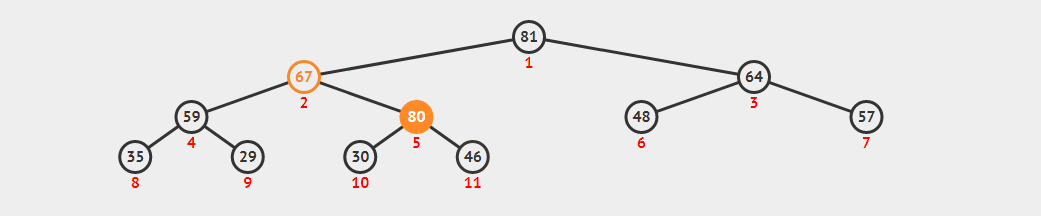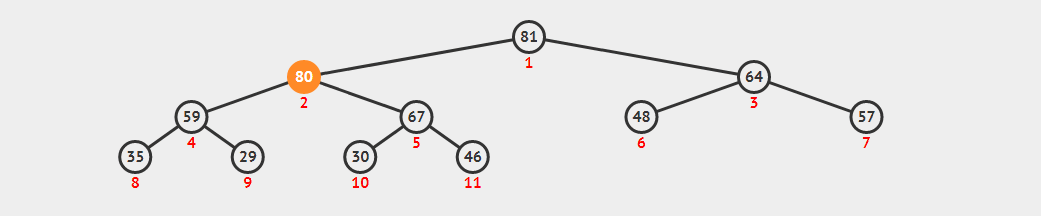
插入操作只能在最末尾的位置进行,这是为来保证二叉树的完全二叉树属性。但此时也可能会破坏最大堆属性,因此插入点可能需要向上移动。这个操作称之为ShitUp或BubbleUp或IncreaseKey。
删除堆顶数据,然后将最末尾数据移动到堆顶,此时会破坏最大堆结构,因此需要向下调整。称之为ShiftDown或BubbleDown或Heapify操作。
在向下调整时,总是和较大的子节点交换。
PQ - 优先级队列
到此,有了Insert(v)和ExtractMax()操作,我们实现了优先级队列。
前中后序遍历
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
| package main
import (
"fmt"
"github.com/straysh/basis_go/datastructure"
)
func main() {
n1 := &datastructure.BTNode{Data: 81}
n2 := &datastructure.BTNode{Data: 80}
n3 := &datastructure.BTNode{Data: 64}
n4 := &datastructure.BTNode{Data: 59}
n5 := &datastructure.BTNode{Data: 67}
n6 := &datastructure.BTNode{Data: 48}
n7 := &datastructure.BTNode{Data: 57}
n8 := &datastructure.BTNode{Data: 35}
n9 := &datastructure.BTNode{Data: 29}
n10 := &datastructure.BTNode{Data: 30}
n11 := &datastructure.BTNode{Data: 46}
n1.Left = n2; n1.Right = n3
n2.Left = n4; n2.Right = n5
n3.Left = n6; n3.Right = n7
n4.Left = n8; n4.Right = n9
n5.Left = n10;n5.Right = n11
preOrder(n1)
}
|
递归法 - 前序遍历
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
| func preOrder(node *datastructure.BTNode) {
if node==nil {
return
}
fmt.Printf("%d ", node.Data)
preOrder(node.Left)
preOrder(node.Right)
}
|
递归法 - 中序遍历
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
| func inOrder(node *datastructure.BTNode) {
if node==nil {
return
}
inOrder(node.Left)
fmt.Printf("%d ", node.Data)
inOrder(node.Right)
}
|
递归法 - 后序遍历
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
| func postOrder(node *datastructure.BTNode) {
if node==nil {
return
}
postOrder(node.Left)
postOrder(node.Right)
fmt.Printf("%d ", node.Data)
}
|
深度优先(DSF) - 前序遍历
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
| func dsf(node *datastructure.BTNode) {
stack := datastructure.NewStackBT(11)
stack.Push(node)
for ;stack.Size() != 0; {
item := stack.Pop()
fmt.Printf("%d ", item.Data)
if item.Right!=nil {
stack.Push(item.Right)
}
if item.Left!=nil{
stack.Push(item.Left)
}
}
}
|
深度优先(DSF) - 中序遍历
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
| func dsfInOrder(node *datastructure.BTNode) {
stack := datastructure.NewStackBT(11)
p := node
for ;p!=nil; {
if p.Left != nil {
stack.Push(p)
p = p.Left
} else {
fmt.Printf("%d ", p.Data)
p = p.Right
for ;p==nil && stack.Size()>0; {
p = stack.Pop()
fmt.Printf("%d ", p.Data)
p = p.Right
}
}
}
}
输出: 35 59 29 80 30 67 46 81 48 64 57
|
深度优先(DSF) - 后序遍历
//todo
广度优先(BSF) - 按层遍历
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
| func bsf(node *datastructure.BTNode) {
queue := datastructure.NewQueueBT(11)
queue.Enqueue(node)
for ;queue.Size()>0; {
p := queue.Dequeue()
fmt.Printf("%d ", p.Data)
if p.Left!=nil {
queue.Enqueue(p.Left)
}
if p.Right!=nil {
queue.Enqueue(p.Right)
}
}
}
|
求树的高度
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
| func btHeight(node *datastructure.BTNode) int {
if node == nil {
return 0
}
return max(btHeight(node.Left), btHeight(node.Right)) + 1
}
|



